During the first day of ISSCC in San Francisco research from Fudan University in Shanghai described a brand new microprocessor that does away with the traditional shared memory architecture.
- Photo courtesy of Fudan
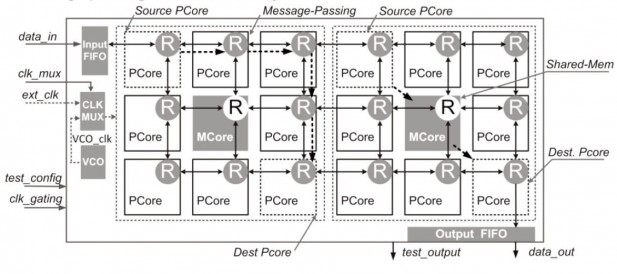
The advantage of using a message passing scheme is that it scales much better than the shared memory. Whereas shared memory relies on software, the message passing scheme has been implemented using mailboxes designed in hardware, according to the research paper that was presented at ISSC.
The processor itself consists of 16 RISC cores that share two small cores for shared memory access, but much of the communication is done using message passing. The processor also does away with the traditional caches and instead implements an extended register file.
The end result is a processor that has been implemented on a TSMC 65nm L CMOS processor and runs at up to 800MHz. When dialed back to 750MHz each core can run at 1.2V and only consume 34mW, which shows that the design is extremely energy efficient. We look forward to seeing this in the wild.S|A
Mads Ølholm
Latest posts by Mads Ølholm (see all)
- Samsung shows off 20nm PRAM - Feb 28, 2012
- DDR4 shows up in the wild - Feb 28, 2012
- SanDisk develops the world’s smallest 128Gb flash chip - Feb 22, 2012
- Aussies create single atom transistor with precise control - Feb 21, 2012
- Chinese 16 core CPU uses message passing - Feb 21, 2012